Friction discs are made of friction materials and bonded, usually with rivets, to a metal plate. These make up the disc brake pads of the brake component. The other parts of a typical disc brake include calipers attached to pistons and rotors which are responsible for motion. Read More…
You only need to know one name for your friction material needs: Cook Bonding & Manufacturing. We have been working hard for over 3 decades and specialize in the manufacture of high quality friction materials, gear tooth facings, press blocks, and more.

As the originators of sintered metallic friction materials, GMP Friction Products develops unique clutch plate and brake pad solutions tailored to our customers` needs. We have a dedicated staff for research and development, devoted to engineering materials that provide the optimum blend of durability and effectiveness. We serve the agricultural, vehicle, aerospace, and other specialty markets.

As a complete friction materials company you can send us your custom fabrication, bonding, relining, riveting, brake lining or clutch assembly questions and we will provide you with fast & competitive quotes. At Phoenix Friction we understand the importance of finding reliable, timely & cost-effective solutions for your friction material problems and that is why strive for 100% customer...

More Friction Disc Manufacturers
Friction Discs: Comprehensive Guide to Function, Materials, and Applications
Friction discs, also known as brake discs or clutch plates, are critical components in a wide range of mechanical systems, most notably in automotive braking systems, industrial machinery, and heavy equipment. Their primary function is to slow down or halt the rotational motion of drive shafts, which, in turn, stops the wheels or moving parts from rotating. This is achieved by the strategic application of friction, converting kinetic energy into heat and thus dissipating motion efficiently and safely.
How Do Friction Discs Work?
When pressure is applied to the brake pedal in a vehicle, the brake calipers clamp the friction discs onto the rotors. This action can be actuated by various power sources depending on the type of system:
- Hydraulic braking systems: Most common in automotive and light truck applications, hydraulic fluid transfers the pedal force to the calipers.
- Mechanical systems: Frequently used in bicycles and some industrial machines where direct mechanical linkage is feasible.
- Pneumatic systems: Common in heavy-duty vehicles, buses, and certain industrial equipment where compressed air actuates the braking mechanism.
Regardless of the actuation method, the principle remains the same: the calipers force the friction discs to close around the rotors, generating enough friction to stop motion. During this process, a significant amount of kinetic energy is transformed into heat energy, which must then be dissipated effectively to maintain system performance and safety.
Want to learn more about the differences between hydraulic and pneumatic brake systems? Explore our in-depth comparison for insights on which type suits your application.
Materials Used in Friction Disc Manufacturing
The choice of materials for friction disc construction is crucial for ensuring durability, optimal performance, and safety. Friction discs are subject to high stress, tension, and extreme temperatures, which makes material selection a key factor in their lifespan and functionality. Here are some of the most common friction disc materials used across industries:
- Ceramic compounds: Renowned for their heat resistance, stability, and long service life. Ceramic friction discs are often used in high-performance vehicles and heavy-duty machinery.
- Organic materials: These include resins, rubber, and composites. While typically used in standard vehicles due to their affordability and quiet operation, they may wear faster under intense use.
- Sintered metals: Created by fusing metallic particles under high heat, sintered friction discs excel in industrial environments that demand high load capacity and durability.
- Woven fibers (e.g., Kevlar, aramid): Known for their lightweight properties and resistance to wear, these are increasingly popular in performance and racing applications.
- Carbon-carbon composites: Extremely lightweight and capable of withstanding ultra-high temperatures, these are primarily found in motorsports and aerospace applications.
It is important to note that asbestos, once a common material in disc and clutch plates, is now largely banned due to the health hazards posed by asbestos dust. Modern friction discs use safer, more environmentally friendly alternatives that do not compromise on performance.
Key Considerations in Material Selection
- Thermal resistance: Can the material handle repeated high-temperature cycles?
- Wear rate: How quickly will the disc material deteriorate under normal and extreme conditions?
- Noise and vibration: Does the material minimize noise, judder, or vibration for a smoother ride?
- Cost-effectiveness: Is the material affordable for both manufacturers and end users?
Curious about which brake material is right for your needs? Compare the properties, pros, and cons of each type to make an informed decision.
Design Variations and Their Impact on Performance
The design of a friction disc is just as important as its material. Disc design directly affects cooling, durability, and the overall effectiveness of the braking or clutch system. Common design variations include:
- Solid discs: Simple, robust, and cost-effective. Ideal for standard applications with moderate heat dissipation needs.
- Vented/slotted discs: Feature internal vanes or slots to enhance airflow and heat dissipation. Common in performance cars and heavy machinery.
- Drilled discs: Perforated surfaces improve heat management and reduce brake fade, making them popular in racing and high-performance vehicles.
- Composite/multi-material discs: Combine different materials to optimize performance characteristics such as weight, strength, and thermal stability.
Properly designed and manufactured discs will wear evenly, ensuring consistent braking and gear changing even as the components approach the end of their service life. Uneven wear or thickness can cause juddering, increased vibration, and even damage to adjacent engine components, reducing both performance and safety.
Need help identifying the best disc type for your vehicle or machinery? Contact our technical team for personalized recommendations based on your specific requirements.
Friction Disc Applications Across Industries
Friction discs play a pivotal role in a variety of sectors, each with its own set of requirements and performance expectations. Some of the most common applications include:
- Automotive industry: Standard and high-performance vehicles, motorcycles, trucks, and buses all rely on friction discs for reliable braking and clutch engagement.
- Industrial machinery: Heavy-duty equipment such as cranes, mining trucks, and manufacturing machinery use robust friction discs to manage large loads and frequent stop-start cycles.
- Aerospace: High-performance carbon-carbon or ceramic discs are used in aircraft braking systems, where reliability and weight savings are critical.
- Railway systems: Trains and trams utilize specialized friction discs to ensure safe, controlled stopping power under varying load and weather conditions.
- Marine applications: Ships and offshore equipment use corrosion-resistant friction discs for propulsion and anchoring systems.
- Renewable energy: Wind turbines and hydroelectric generators employ friction discs to control rotational speed and manage mechanical loads.
- Motorsports: Racing vehicles require lightweight, high-temperature friction discs for optimal performance during intense driving conditions.
Are you searching for friction discs tailored to a specific application? Browse leading friction disc manufacturers or request custom solutions for unique industrial needs.
Benefits of High-Quality Friction Discs
Choosing the right friction disc is essential to maximize system efficiency and ensure long-term safety. Here are the key benefits of investing in high-quality friction discs:
- Improved stopping power: High-performance friction discs deliver responsive, consistent braking and clutch engagement, reducing stopping distances and enhancing safety.
- Longer lifespan: Durable materials and precision manufacturing increase the operational life of the discs, reducing maintenance costs and downtime.
- Enhanced heat dissipation: Advanced designs and materials minimize heat buildup, reducing the risk of brake fade and component failure.
- Reduced noise and vibration: Quality discs are engineered to minimize noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH), improving driver and operator comfort.
- Lower total cost of ownership: Fewer replacements and lower maintenance requirements translate to significant long-term savings.
Common Issues and Maintenance Tips for Friction Discs
Despite their robust construction, friction discs are subject to wear and tear over time. Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting can help prevent serious problems and maximize the efficiency of your braking or clutch system. Here are some common issues and best practices for maintenance:
- Uneven wear or thickness variation: Can result in juddering, vibration, and reduced braking performance. Regular inspection and timely replacement are crucial.
- Overheating: Prolonged high-temperature exposure can cause glazing, reduced friction, and even structural failure. Ensure proper cooling and avoid excessive load when possible.
- Dust accumulation: As friction discs wear, they generate dust that can impact performance and, if inhaled, pose health risks. Use appropriate cleaning procedures and wear protective gear during maintenance.
- Corrosion: Especially in marine or humid environments, corrosion can compromise disc performance. Choose corrosion-resistant materials and apply protective coatings where needed.
Need step-by-step instructions on replacing worn friction discs? Check out our detailed replacement guide for both DIY enthusiasts and professional mechanics.
Friction Disc Selection Guide: How to Choose the Best Disc
Selecting the right friction disc involves considering several factors that affect performance, safety, and cost. If you are evaluating options for your vehicle, industrial equipment, or other machinery, ask yourself the following questions:
- What is the primary application (e.g., automotive, industrial, marine, motorsports)?
- What load and temperature conditions will the disc be exposed to?
- Is noise reduction or smooth operation a priority?
- What is your preferred maintenance schedule and replacement interval?
- Do you require special certifications or compliance with industry standards?
- Are there any size, weight, or installation constraints?
- What is your overall budget for initial purchase and long-term maintenance?
By addressing these questions, you can narrow down your options and select the most suitable friction disc for your needs. For further assistance, consult with a technical specialist who can provide tailored recommendations based on your application.
Frequently Asked Questions About Friction Discs
- What is the difference between a friction disc and a brake pad? Friction discs (or rotors) are typically used in disc brake systems, while brake pads press against the disc to generate friction.
- How often should friction discs be replaced? Replacement intervals depend on usage, material, and application, but regular inspection is recommended every 12,000 to 15,000 miles for automotive discs.
- Can I upgrade to high-performance friction discs? In many cases, yes. Upgrading to drilled, slotted, or ceramic discs can improve performance, especially in demanding environments.
- Are there environmentally friendly friction disc materials? Yes, modern discs utilize non-asbestos organic, ceramic, and metallic compounds that are safer for the environment and human health.
- What are the signs of worn or damaged friction discs? Look for reduced braking performance, increased noise or vibration, visible cracks or grooves, and uneven wear patterns.
- How do I clean and maintain my friction discs? Regularly remove dust and debris, inspect for damage, and follow manufacturer guidelines for cleaning agents and procedures.
Friction Discs: The Future of Braking and Clutch Technology
The field of friction disc technology is continually evolving, with ongoing research into new materials, manufacturing processes, and design innovations. Emerging trends include the development of:
- Advanced composite materials for even greater heat resistance and weight reduction.
- Nanotechnology coatings to enhance wear resistance and reduce maintenance needs.
- Smart sensor integration for real-time monitoring of disc temperature, wear, and performance.
- Eco-friendly formulations that minimize environmental impact while maximizing safety and efficiency.
As the demand for higher performance, safety, and sustainability rises, friction disc manufacturers are investing in R&D to deliver products that meet the evolving needs of automotive, industrial, aerospace, and energy sectors.
Find the Right Friction Discs for Your Application
Whether you are a fleet manager seeking durable discs for commercial vehicles, an engineer specifying clutch components for industrial automation, or a motorsports enthusiast upgrading your track car, selecting the right friction disc is a crucial decision. Consider your unique requirements and take advantage of the latest advancements in friction disc technology to optimize performance and safety.
Ready to compare leading friction disc suppliers and manufacturers? Start your search here for detailed product reviews, technical specifications, and expert buying tips.
Conclusion: Maximizing Performance with Quality Friction Discs
Friction discs are foundational to modern braking and clutch systems, playing an essential role in safety, efficiency, and equipment longevity. By understanding how friction discs work, the materials and designs involved, and the factors influencing selection and maintenance, you can make informed decisions that optimize your system’s performance and value.
For more insights, explore our comprehensive resources on brake materials, leading friction disc manufacturers, and maintenance best practices.
Have a question or need technical support? Contact our team or schedule a consultation with our brake and clutch technology experts today.




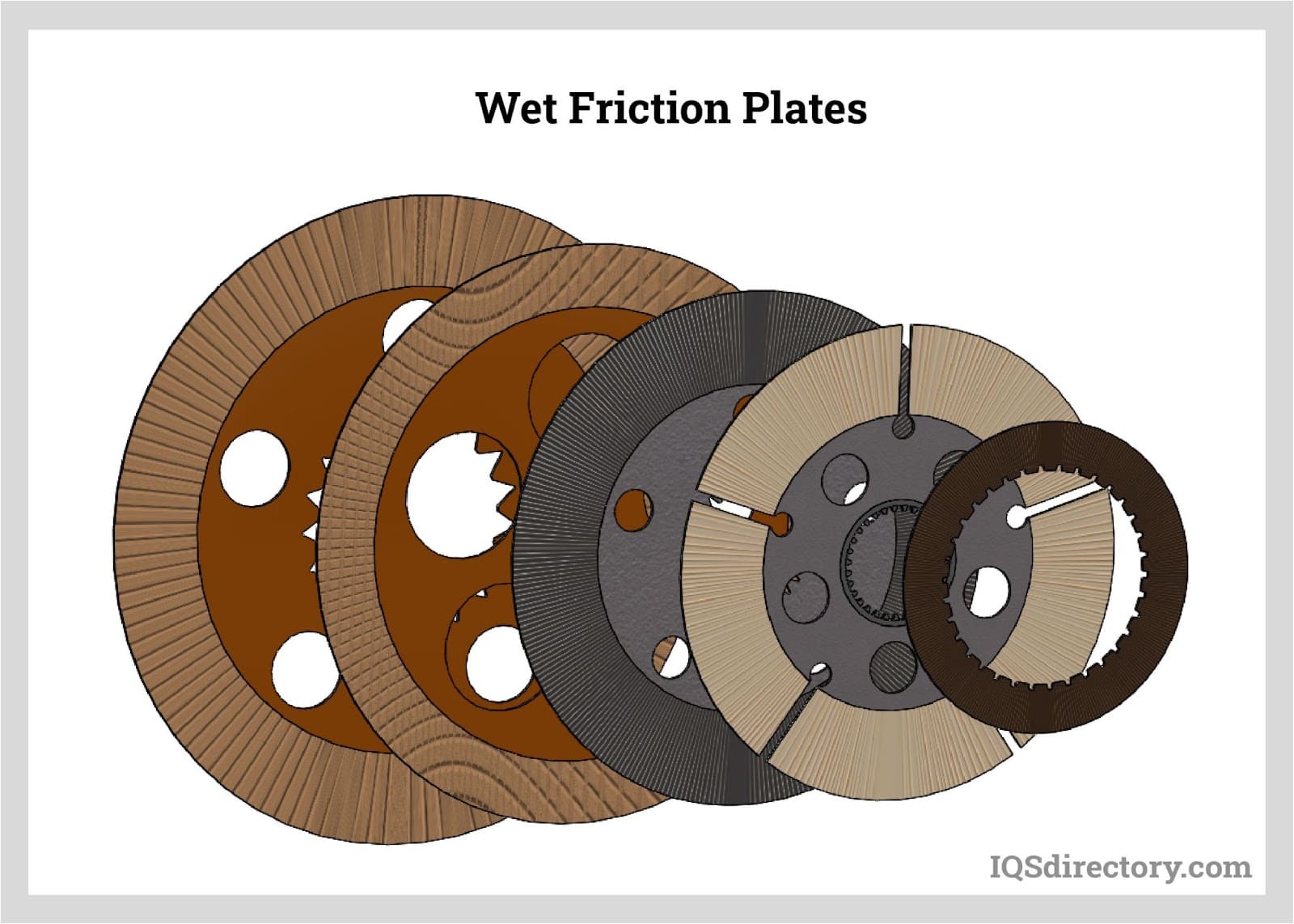




 Ball Bearings
Ball Bearings Ball Screws
Ball Screws Electric Motors
Electric Motors Friction Materials
Friction Materials Gears
Gears Quick Release Couplings
Quick Release Couplings Shaft Couplings
Shaft Couplings Speed Reducers
Speed Reducers Timing Belting
Timing Belting Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services